Effects of fertilizer with gypsum as its main raw material
Three major elements of fertilizer and trace elements
Fertilizer is essential for growing crops!
If the necessary nutrients are insufficient in the crops, growth will be bad or failure will occur. Among various nutrients, nitrogen, phosphoric acid and potassium are particularly important and are said to be the three major elements.
In addition, nutrients such as calcium, magnesium, sulfur, and iron are necessary, but as they only have small amounts, they are said to be trace elements. However, if one of these elements is insufficient, even if there are enough other elements, it will affect crop growth and in some cases will cause yield deficiency.

Cabbages

Grass pasture
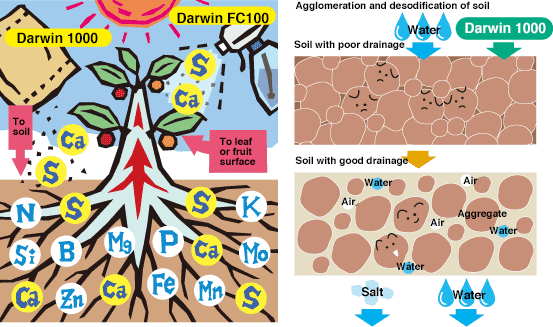
Function of calcium
Calcium is important as a component that makes human bones and teeth strong, and at the same time it has a function to firmly fix cells and cells for crops, and a component essential for nurturing crop growth
Function of sulfur
Components indispensable for traits such as proteins, amino acids, vitamins
The effect of "Darwin" fertilizer
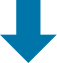
"Darwin", which has calcium sulfate (gypsum: CaSO4) as its main ingredient, is an effective fertilizer, calcium fertilizer containing calcium (Ca) and sulfur (S). There are types that are used by spreading it on the soil and types that are sprayed on the foliage and fruit surface. You can expect further growth of crops by combining them. Moreover, we can expect not only fertilizer effect, but also effect to make rich soil by modifying the land where crops are difficult to grow due to salt damage. (Soil improvement: agglomeration and desodification)
Although the calcium content is adequately contained in the soil examination, crops tend to be deficient in calcium, the soil becomes alkaline, and the growth of the crop becomes worse.
・ Calcium is not effective
↓
Caused by water-soluble calcium deficiency
・ Becomes alkaline
↓
Caused by excessive use of quicklime, slaked lime, charcoal, shellfish
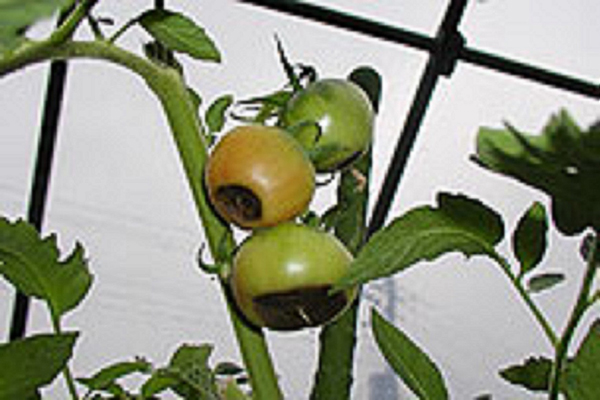

Calcium-deficient tomato
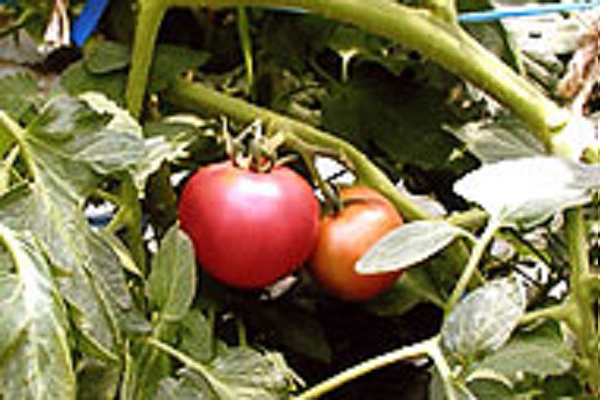

Darwin fertilized tomatoes
- Soluble in water (solubility)
- Should not significantly affect soil pH level
- Should not cause chemical damage
- Easy to handle and store, and safe calcium (stability)
"Darwin (calcium sulfate)" is the most suitable!
Comparison with other calcium resource
| Particular | Darwin | Calcined lime | Hydrated lime | Calcium carbonate |
Fossilized seashell | Calcium phosphate |
Calcium chloride |
Calcium nitrate |
Magnesia lime |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Principal component chemical formula |
Calcium sulfate CaSO4 |
Calcium oxide CaO |
Calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2 |
(Limestone)CaCO3 | Calcium carbonate CaCO3 |
Calcium hydrogen phosphate CaHPO4 |
CaCl2 | CaNO3 | Calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate |
| Solubility in 100g of water |
0.22g | 0.13g | 0.19g | 0.002g | 0.002g | 0.02g | 59.5g | 226g | 0.03g |
| PH in the soil | Neutral | Strong alkali | Strong alkali | Weak alkali | Weak alkali | Neutral | Neutral | Neutral | Weak alkali |
| Thickening effect component | Calcium Sulfur |
Calcium | Calcium | Calcium | Calcium | Calcium Phosporic acid |
Calcium | Calcium Nitrate Nitrogen |
Calcium Magnesium |
| Stability | Stable | Reacts with water Correlate with heat |
Hygroscopic | Stable | Stable | Stable | Large hygroscopicity |
Large hygroscopicity |
Stable |
| Presence or absence of excessive fault |
None | Present | Present | None | None | None | Present | Present | None |
| Designation of fertilizer method |
Designated as special fertilizer | Designated as ordinary lime-based fertilizer |
Designated as ordinary lime-based fertilizer |
Designated as ordinary lime-based fertilizer |
Designated as ordinary lime-based fertilizer |
Designated as ordinary phosphate- based fertilizer |
Designated as special calcium fertilizer |
Designated as ordinary nitrogen- based fertilizer |
Designated as ordinary magnesia fertilizer |
