Fire resistance
Why it will not burn? “Fire resistance”
Gypsum is strong against fire. The secret is in crystallized water equivalent to about 21% of its weight.
This crystallized water is very stable in normal condition and does not disperse, but once it comes in contact with the heat of fire it will cause thermal decomposition and start to evaporate. The temperature of gypsum does not rise above a certain temperature until all of the crystallized water evaporates into water vapor and is released. To put it in simple words, imagine the same phenomenon that when you blow a flame with a burner onto a lump of ice, that part gradually dissolves into water and the ice temperature is kept below 0°C until all the ice melts.
Gypsum board contains 21 percent
of crystallized water.
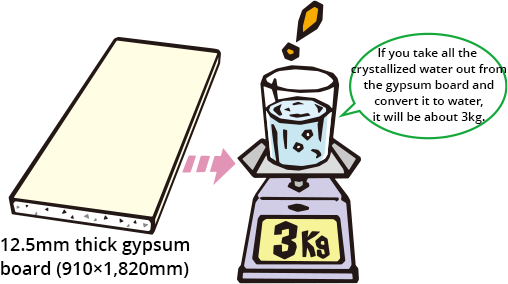
Crystallized water contained in the gypsum
board fulfills the role of "firefighter".
- 1 layer of 12.5mm thick gypsum board:15 minutes
- 4 layer of 12.5mm thick gypsum board:60 minutes
Fire resistance regulations in the Building Standards Act
- The fire resistance requirement for each part of fire resistant building is prescribed in Article 107 of the Building Standards Act Enforcement Ordinance.
- Fire resistance requirement is classified into damage resistance, thermal insulation, and flame retardancy, and fire-resistant time is specified for each part.
-
According to the Building Standard Act, it regulates that fire partition compartments should be provided to prevent the spread of fire and the transmission of smoke.
It also regulates that columns and beams should be encased with fire resistant materials to prevent collapse of building due to fire.
Technical standard on fire resistance performance
| Structural part | Fire resistant structure (Article 2 clause 7 of the Act) | ||||
| Floors where the number of floors counted from the top floor is more than 2 and less than 4, including the top floor itself (Article 107 of the Ordinance)
A |
Floors where the number of floors counted from the top floor is more than 5 and less than 14 (Article 107 of the Ordinance)
B |
Where the number of floors counted from the top floor is more than 15 (Article 107 of the Ordinance)
C |
|||
| Partition Walls | (Non-loadbearing wall) | 1 hour | 1 hour | 1 hour | |
| (Limited to shear wall) | 1 hour | 2 hour | 2 hour | ||
| Outer wall | Shear walls | 1 hour | 2 hour | 2 hour | |
| Non-loadbearing wall | Parts where there are risk of fire spreading | 1 hour | 1 hour | 1 hour | |
| Parts other than the above | 30 minutes | 30 minutes | 30 minutes | ||
| Column | 1 hour | 2 hour | 3 hour | ||
| Floor | 1 hour | 2 hour | 2 hour | ||
| Beam | 1 hour | 2 hour | 3 hour | ||
| Roof | 30 minutes | ||||
| Staircase | 30 minutes | ||||
| Related designated structure | Ministry of Construction Public Notice No. 1399 Year 200 | ||||
* “Ministry of Construction” is the former name of the current “Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT)”
Fire partition
A section to prevent fire from spreading and to secure an evacuation route. (Building Standard Act Enforcement Ordinance, Article 112)
Regarding certification of fire resistance by the Minister of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism
Fire resistance of walls, floors, ceilings, pillars, etc. is certified by performing fire resistance tests at a public laboratory and satisfying certain criteria (fire resistance requirements).
Classification of fire resistance performance requirements
| Damage resistance | Performance that does not cause deformation, melting, destruction or other damage |
|---|---|
| Heat insulation | Performance to prevent the temperature on the non-heated side rising above the ignition temperature of combustible matter |
| Flame retardancy | Prevents occurrence of cracks or other damage that will cause the fire to spread from the indoor side to the outdoors |
